Fish Families Family Identification. - ppt video online download
Acipenseridae / Sturgeon Family:
Fish Families Family Identification.
Rows of bony scales. Ventral Mouth, with barbels. Lake Sturgeon in the Great Lakes. Flesh is tasty!
Long dorsal fin across most of the back. Body covered with scales. Long bony plate under the lower jaw. Only one species exists living fossil
Anguillidae / Freshwater Eel Family
The American Eel is distinguished by its shape. Long dorsal, caudal and anal fins. Toothed jaws, and the single gill opening. Lampreys have a similar shape and long dorsal fins but have no jaws (teeth are in a sucking disc) and there are 7 gill openings – Lamprey NOT included with this group. Found in N. Atlantic and Great Lakes Region.
Atherinidae / Silverside Family
Brook silversides are known for leaping out of the water over and over again-especially on moonlit nights. Brook silversides are small, almost see-through fish that grow to about 3 long.
Catostomidae / Sucker Family
Single soft rayed dorsal fin. Toothless jaws, teeth in throat only. Cycloid scales. Fleshy, protruding lips.
Centrarchidae / Sunfish Family
Deep-bodied and compressed laterally. Fins often have both soft rays and stiff spines. Sunfish generally thrive in warm water. All sunfish are nest builders, and their saucer-shaped nests can be frequently observed along the shoreline of ponds, lakes and streams in late spring. An active, nest-guarding male can often be observed swimming within the nest vicinity, guarding both eggs and newly-hatched young. A few days after hatching, the young emerge from the nest, at which time the guarding parent leaves them to care for themselves. All sunfish are carnivorous.
Cottidae – Sculpin Family
Large head. Fanlike pectoral fins. No spines in anal fin. This is a very large family with about 300 species. Most species are found in Arctic or temperate waters and are bottom dwellers. They typically occur in shallow or inter-tidal zones, though some species occur in deep ocean and others in fresh water.
Cyprinidae – Minnow Family
No jaw teeth, ONE dorsal fin. 1-3 rows of pharyngeal teeth. Barbels sometimes present. This huge family lives almost exclusively in freshwater, though some of its members stray into brackish water. There are more than two thousand species in this family.
Members of the pike family have a long, streamlined profile that is found among predators in many fish families throughout the world. Their fins are soft rayed, lacking the stiff spines found in other familiar fishes, such as sunfish and yellow perch. Median fins include the dorsal and anal fins, located opposite each other about three-quarters of the way back towards the tail. The pelvic fins are located midway on the fish s belly. The pectoral fins are positioned closer to the head.
Because they are such aggressive predators, they are also popular fish for anglers to catch.
Gasterosteidae / Stickleback Family:
Sticklebacks are small fish. They have 2,3 or more strong spines on the back in front of the dorsal fin. (spines that they can erect or depress at will) Some of them have bony plates in the scaleless skin, but others do not.
Found in marine (salt), brackish (mixed) & freshwater habitats in the northern hemisphere. Spawning almost always takes place in freshwater. Eggs usually develop in a nest built & guarded by the male.
Catfish do not have scales, and are aged by making cross sections of the pectoral spines to read growth rings. The fin spines can be very toxic because of poisonous cell secretions on the spine but are not fatal to humans. Wounds can be painful and extremely swollen for days although in most cases the wasp-like sensation fades after an hour and is gone in about 4-5 hours. Madtoms are named for their hyperactive, darting and dashing behavior. Bullhead catfishes are hardy and very tolerant of domestic pollution. FYI:Larger catfishes, such as the Channel Catfish, are commercially important in the U.S.A. and are cultured in ponds. Catfish restaurant dinners are a specialty in the southern U.S.A. and catfish figure prominently in fish and chips. These fishes are also sought after by anglers, being strong fighters and good eating.
The barbels and skin are taste and touch sensitive and used to detect food. This is particularly useful in muddy water and at night. Many of these catfishes are nocturnal. Taste can also be used in breeding behavior and in schooling . Most catfish also have excellent hearing!
Gars are found in freshwaters of North America sometimes in brackish water & rarely the sea. Gars have elongate jaws ( gar is Old English for spear) filled with needle-like teeth. The ganoid scales are heavy, peg and groove hinged, non-overlapping, rhombic and plate-like, forming an effective armor. Dorsal and anal fins are near the tail.
They have been pursued by anglers who specialize in trying to catch this species with its narrow bony mouth. They are edible, better tasting when smoked, although they are hard to clean because of the bony armor. The flesh must be carefully cleaned of the eggs before eating as these are thought to be poisonous although there is some dispute about this.
Perches have 2 dorsal fins, the first spiny & the second soft rayed, which are usually separate or only slightly joined. The anal fin has only 1-2 spines (rather than 3 as in related families). The pelvic fins are under the pectorals. Scales are ctenoid.
The operculum has a sharp spine. There are 2 kinds of perches – large species with compressed bodies and a swim-bladder, small species with depressed bodies and reduced or absent swim-bladders. In North America the larger species include the Yellow Perch, Sauger and Walleye. The smaller species are the darters. Darters are sensitive to environmental change and are useful indicators of the health of aquatic ecosystems.
The Trout-perch Family contains only 2 species in North American freshwaters. The name derives from their anatomy, which contains characters of both the trout or salmon-like fishes and the perch-like fishes. They include an adipose fin, weakly ctenoid scales, a scale-less head.
Lampreys are jawless fishes. Lacking bone in the skeleton. 7 pairs of pore-like gill openings. The eel-like body has no pectoral or pelvic fins. There are 1 or 2 dorsal fins and a caudal fin. The mouth is a circular armed with rows of sharp teeth.
There is a light-sensitive pineal organ or third eye behind the nostril. The skin is covered in mucus which is poisonous to fishes and humans. Lampreys are edible if the mucus is cleaned off.
Polyodontiae / Paddlefish Family:
Long, flattened, paddle-like snout. Large head · Small eyes · No teeth. Two barbels under the snout near the mouth.
The huge snout covered with sensitive taste buds which may help locate plankton. A filter-feeder, the paddle fish can grow up to 200 pounds. Dams have caused a decrease in population in the United States.
Have an adipose fin. Scales are cycloid. There are no fin spines. The lateral line is obvious , dorsal fin at mid-body. Breeding tubercles may in some species. These fishes are tetraploids.
Many are anadromous, spending part of their life at sea, but returning to freshwater where all species spawn in a gravel bed in rivers or stream. Most die after spawning.
It is fairly tolerant of low oxygen concentration. Sometimes the only, or one of a very few, fish species left in waters susceptible to winter or summer kill.
It burrows tail-first in mud allowing it to live in waterways unavailable to other fishes. It is eaten by many species of fish such as grass pickerel, sunfishes, northern pike, and catfishes; it is also preyed upon by birds, foxes, and snakes.
Central mudminnows are known to eat a large variety of zooplankton and benthic and macroinvertebrates. Adults are also known to feed energetically in the winter months on littoral fish. Uses a modified gas bladder to breathe air pockets trapped between the ice and water during the winter to feed and stay active.
Bowfin, paddlefishes, gars and sturgeons. Placoid. They do not increase in size as the fish grows, instead new scales are added. Often referred to as denticles. sharks and rays.
Found in the most bony fishes. Overlapping scales. Gives the fish greater flexibility than in those species with placoid or ganoid scales. Ctenoid.
Placoid Scales Cycloid Scales Ganoid Scales Ctenoid Scales
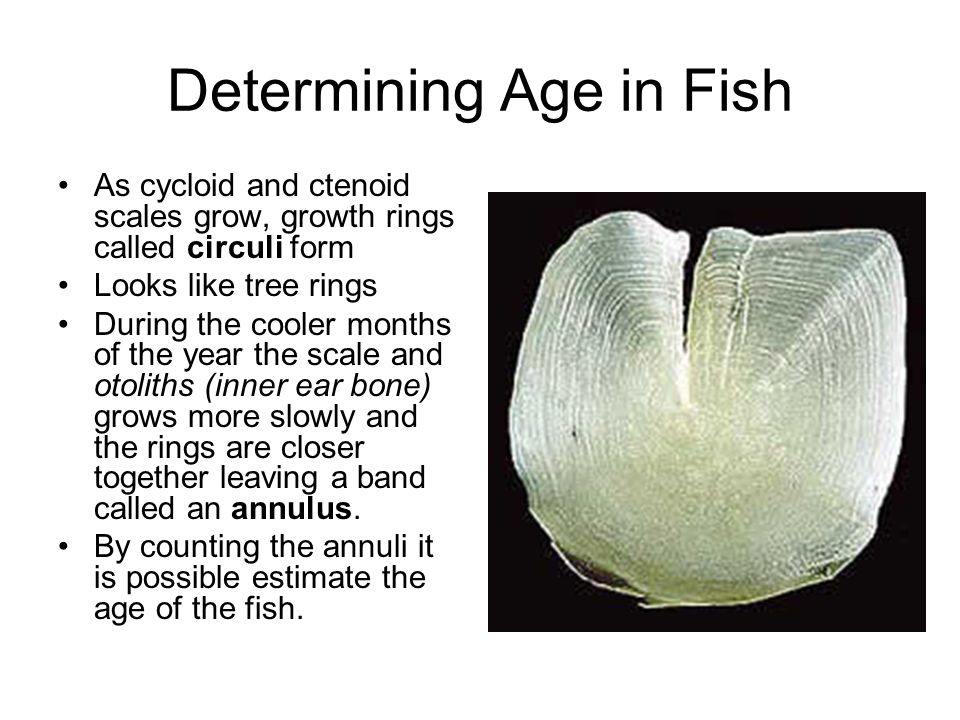
As cycloid and ctenoid scales grow, growth rings called circuli form. Looks like tree rings. During the cooler months of the year the scale and otoliths (inner ear bone) grows more slowly and the rings are closer together leaving a band called an annulus. By counting the annuli it is possible estimate the age of the fish.
Tetraploid: Having 4 sets of chromosomes in the nucleus. Anadromous: Fishes that spend all or part of their adult life in salt water and return to freshwater streams and rivers to spawn. Catadromous: Fish that journey from freshwater to the depths of the ocean to spawn.
#1 What Fish is this #2 What Family
#4 What is the fish name (common name)
Same fish – different pictures. Note: Fish is large – not found in streams – found in lakes.
#9 Fish Name (Same one that Becca brought in) #10 Family Name
RELAX – You can do this says Gill (Moorish Idol)
16 (tail fin or ___ fin) 15 (bony plate) 18 17
#19. A person that studies fish is called a/an ___.

Fish Families Family Identification. - ppt video online download

Selected Fish Families from the Order Perciformes

PPT - Fish Identification for Common Fish Species of Rock Creek Park PowerPoint Presentation - ID:4323682

Jellyfish genomes reveal distinct homeobox gene clusters and conservation of small RNA processing

PPT - GO FISH PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2890384

Fish Families Family Identification. - ppt video online download

PPT - IDENTIFICATION OF FISHES PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID :3395442

Fish family carangidae

Ocean Life PowerPoint, World Ocean Day

Family carangidae hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy
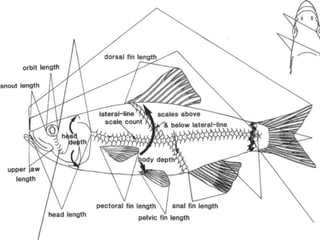
Identification of Fish Species