Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes - ppt video online download

Introduction to Vertebrates Phylum - Chordata. Subphylum – Vertebrata Recall- All Chordates share the following characteristics: -Notochord -Dorsal hollow nerve cord -Pharyngeal gill slits -Post-anal tail
Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes
With introduction to vertebrae classes. Sources: Modern Biology- Holt, Reinhart & Winston. ocw.tufts.edu/Content/5/Lecturenotes/ Mrs. Lori Schalles. Biology II. Ringgold High School.
Phylum - Chordata. Subphylum – Vertebrata. Recall- All Chordates share the following characteristics: -Notochord. -Dorsal hollow nerve cord. -Pharyngeal gill slits. -Post-anal tail.
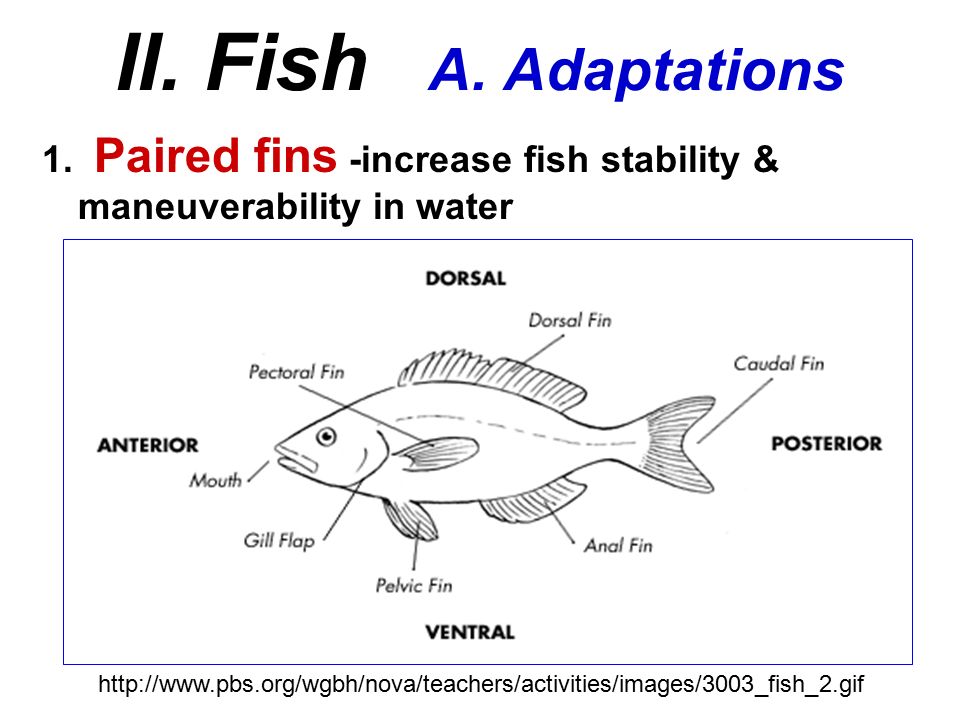
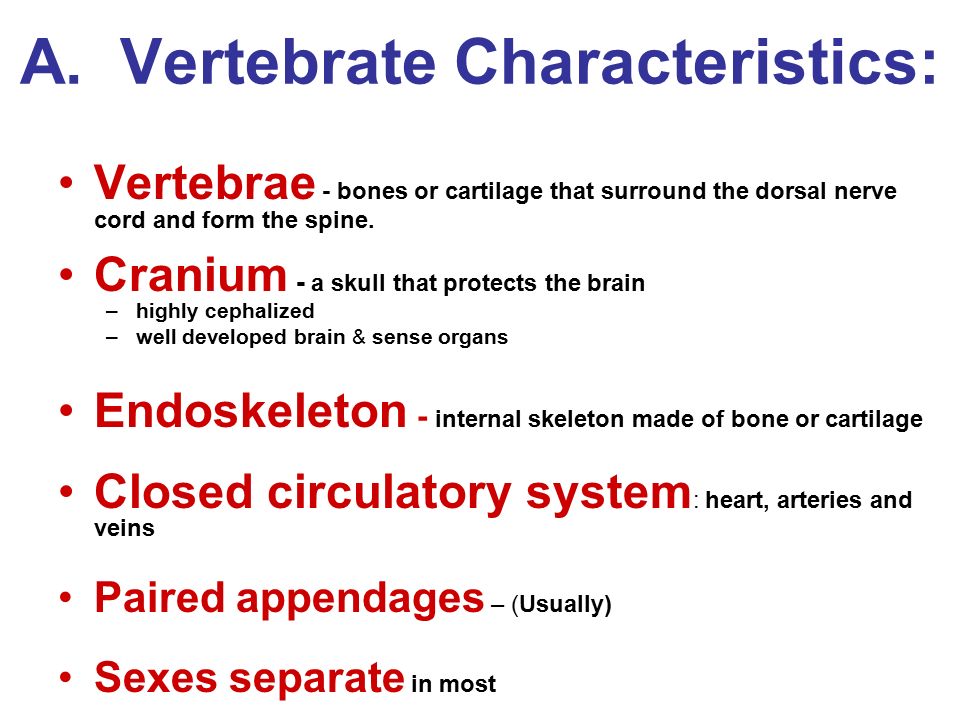
Vertebrae - bones or cartilage that surround the dorsal nerve cord and form the spine. Cranium - a skull that protects the brain. highly cephalized. well developed brain & sense organs. Endoskeleton - internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage. Closed circulatory system: heart, arteries and veins. Paired appendages – (Usually) Sexes separate in most.
Myxini - hagfishes. Cephalaspidomorphi - lampreys. Chondrichthyes - sharks, rays, skates. Actinopterygii - ray-finned fishes. Sarcopterygii - lobe-finned fishes. Amphibia - frogs, toads, salamanders. Reptilia - lizards, snakes, and turtles. Aves - birds. Mammalia - mammals.
The first fish were jawless. About 450 million years ago, the first fishes with jaws and paired fins appeared. Jaws are thought to have evolved from the first pair of gill arches, the skeletal elements that support the pharynx.
Pectoral fin : counteract. Pelvic fin : stabilizer. Caudal fin : Motor. Anal fin : Stabilizer, Gonopodium (modified for transferring sperm in live bearers)
Ctenoid- thin & hair –like ends. Cycloid- thin with smooth edges. Ganoid – thick & heavy. Mucous (glycocalyx) Full of antibiotic / antifungal enzymes and antibodies. Protective coating. Slough off pathogens. Can be detrimental in high amounts. Alarm cells (pheromone)
Streamlined body plan – (allows fish to move rapidly in water) Adaptations for buoyancy. stored gases (swim bladder or lung) lipids help maintain vertical position in water. Efficient respiration - gills exchange gases. Homeostasis - concentration of solutes. in a fish’s body usually differs from that of the water. have adaptations to maintain ion and water concentration.
Sight: fish eyes like eyes of land vertebrates. Sound: internal ears hear. Nostrils & Tastebuds. chemoreception (detect chemicals) senses of smell and taste. Tastebuds may be located in mouths, lips, fins, and skin, and on whisker-like organs called barbels.
picture from: NOTE: some fish have the ability to detect electrical and magnetic fields: example- Ampulae of Lorenzini: cartilaginous fishes have sense organs that can detect weak electrical fields.
Figure Lateral line system. (baroreception) Electroreceptors. (Amupullae of Lorenzini)
Also known as slime eels Hagfish burrow into. & eat dead fish. b. Cephalaspidomorphi (Lampreys) Parasitic Lampreys attach themselves to their host with disc-shaped mouth & feed on host’s blood. oceanexplorer.noaa.gov//media/hagfish.html.
Class Cephalaspidomorphi - The Lampreys
Myxine glutinosa, is covered with. special glands that emit sticky slime. In fact, a single hagfish can produce. enough slime at one time to fill a milk jug. The slime covers enemy fish & chokes them to death because they cannot breath. Sometimes the hagfish makes so much slime it covers its own body- then it ties itself into a knot to wipe off the slime.
Class Myxini - The Hagfishes
Skeleton -composed of cartilage (soft, flexible lightweight tissues made of cells & protein) Skin is covered with placoid scales- (small tooth-like spines which reduce turbulence, increase swimming efficiency) Respiration- gills. Excretion- convert ammonia to urea. Reproduction-internal fertilization. Most lay eggs, some live birth. No parental care. -
Figure Clearnose Skate Southern Stingray
Tens of thousands of people come in close contact with sharks each year while swimming, surfing, or boating, numbers of shark attacks are negligible. In 2005, there were 58 confirmed unprovoked shark attacks in the world, resulting in 4 deaths. Good site: 1,600 people are bitten in New York City, by other people, every year. In the U.S., your chances of getting killed by lightning are 30 times greater than dying of a shark attack. Bees, wasps, and snakes kill more people each year than sharks. Tips for Avoiding Attack. Stay out of the water at night, dusk, or dawn. Sharks are most active at night. Swim in a group. Sharks prefer to attack lone victims. Keep close to shore. It will be easier for help to reach you in an attack. Avoid sandbars and sharp drop-offs where fish congregate. Stay out of polluted or murky water. Avoid areas being used by fishermen. Be wary of feeding birds, or porpoises, which indicate the presence of fish. Do not swim if you are bleeding. Sharks can detect tiny amounts of blood. Do not wear shiny jewelry; underwater it resembles fish scales. Avoid bright swimsuits and uneven tanning. Contrasts attract sharks. Do not splash a lot, since it attracts sharks.
EUGENIE CLARK WITH BULL SHARK (MEXICO)
EMBRYO AND YOLK SAC - SWELL SHARK EGG CASE (JAPAN)
Shark from the Inland Sea: Cretoxgrhina Mantelli (Niobrara Formation In Kansas)
2. lungs or swim bladder. 3. bone in the skeleton. 2 types: A. Lobe-Finned Fishes. B. Ray-finned fishes.
Extinct lobe-fin fish may have been ancestors of amphibians. Groups alive today. 1 species coelacanth. 6 species lungfish. (can gulp AIR into lung. as Oxygen source) www2.dpi.qld.gov.au/far/12588.html.
SINGLE SPECIES - LATIMERIA CHALUMNAE.
Includes most. familiar fish: Yellow perch, trout, salmon, guppies, goldfish, herring,& eels.
Operculum -a hard plate that opens at the rear and covers & protects the gills. Circulatory system. heart has two chambers in a row. Blood from the body enters the sinus venosus, moves into the atrium, then into the ventricle. From the ventricle it enters the conus arteriosus, and then goes to the gills. Note the thick walls of muscle for pumping.
Water flows across the gill filaments in a direction opposite to blood flow. Countercurrent flow allows more oxygen to diffuse into the blood than if blood and water flowed in the same direction.
(counter-current flow) Construction of a. single gill filament with. numerous, disc-shaped lamella. oriented parallel to water flow.
Skeleton: The major parts of a fish’s skeleton are the skull, spinal column, pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, and ribs
Adjusts fish overall density by regulating gas in the swim bladder. Thin walled sac in abdominal cavity. Contains mix of gases (oxygen, CO2, Nitrogen) obtained from the Bloodstream. Probably evolved from balloon-like lungs. Can amplify sound in some fish.
filter chemical wastes from the blood. form urine, a solution containing ammonia, ions such as salts, and water. The gills. also allow wastes to diffuse from the blood into the water. help regulate ion and water balance in fish.
Nervous system. Includes brain, spinal cord, nerves & sensory organs. See page 792 for location & function of olfactory bulbs, cerebrum, optic tectum, cerebellum & medulla oblongata. 2 methods of Reproduction. 1. spawning. -most bony fish reproduce by external fertilization (some internal) 2. Some fish bear live young. Example- guppies. -can store sperm & have up to 4 pregnancies from one deposit. Additional Info-
Chondrostei : Sturgeons (think caviar…..) Atlantic Sturgeon - Eastern rivers in North America.
Yangtze River drainage in China) - large bill used to. stir bottom and expose food.
For list of Endangered & Threatened Species of Pennsylvania - Fish, Amphibians and Reptiles go to O2 is as important to fish as to terrestrial animals. If Oxygen poor water, fish will die. Osmotically unfriendly , (H2O is 800 times denser than air) Water is a soup of pathogens ocw.tufts.edu/Content/5/Lecturenotes/
National Geographic Video-Over Fishing. How to Help: Safe, Sustainable Seafood:
China, Russia, and Korea- alien to PA. The air-breathing, land-crawling, voracious predator found in a pond in Crofton, Maryland, is now multiplying into PA. The fish s ability to breathe out of water and travel across land has increased the sense of urgency among wildlife officials. IF YOU CATCH ONE- dispose of them properly. Anglers suspecting they have caught a snakehead are encouraged to NOT release it, and report it to theCommission at or via . PA REGULATIONS. It is unlawful for a person to possess, sell, purchase, offer for sale or barter live snakehead species in Pennsylvania.
By Pittsburgh Zoo Staff. Weight -up to three pounds. Length -8 to 15 inches in length. Can live up to 8 years. Red-bellied piranhas live in the warm fresh water regions of South America. Feed on fish, birds, reptiles, rodents, and small mammals. The name South American native language Tupi-guarani and means cuts the skin. It is illegal to keep piranhas in 21 states of the United States. A school of these 8- to 12-inch fish, have been observed gnawing a 400-pound hog to the bone in minutes (from the Book of Facts )
April 6, 2007—A handful of Christians preparing rockfish as part of their traditional fish dinner this Good Friday might be feasting on one of the oldest creatures ever to live in Alaskan waters. Commercial fishers in the Bering Sea recently hauled in the female shortraker rockfish seen above, which scientists say was between 90 and 115 years old. Researchers at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) used growth rings in the fish s ear bone, or otolith, to make their age estimate.
Oily / fatty fish. White / non-oily fish. Salmon Trout Mackerel Herring Sardines Pilchards Kipper Eel Whitebait Tuna (fresh only) Anchovies Swordfish Bloater Cacha Carp Hilsa Jack fish Katla Orange roughy Sprats. Cod Haddock Plaice Coley Whiting Lemon sole Skate Halibut Rock salmon/Dogfish Ayr Catfish Dover sole Flounder Flying fish Hake Hoki John Dory Kalabasu Ling Monkfish. Parrot fish Pollack Pomfret Red and grey mullet Red fish Red snapper Rohu Sea bass Sea bream Shark Tilapia Turbot Tinned tuna Marlin. Oily fish are all rich sources of. omega 3 fatty acids, which help. prevent heart disease.
But more than just the money- it could cost your life! It has a deadly poison (tetrodotoxin) in its organs. Chefs must take intensive courses & pass exam to become licensed. Only 30% of the applicants pass the test! Several people die each year from eating this fish. If an ingested dose of the fugu s poison is lethal, as more and more muscles are paralyzed, symptoms may include dizziness, exhaustion, headache, nausea or difficulty breathing. For 50 to 80% of the victims, death follows within four to 24 hours. To learn more on FUGU
Fish and shellfish are an important part. of a healthy diet. Contain protein & omega-3 fatty acids, are low in saturated fat. However, nearly all fish and shellfish contain traces of mercury. What is mercury and methylmercury Mercury occurs naturally in the environment. Can be released into air by industrial pollution. Mercury falls from the air and can accumulate in streams and oceans and is turned into methylmercury in the water. This type of mercury can be harmful to unborn babies & young child. Fish absorb methylmercury as they feed & it builds up in them. It builds up more in some types of fish and shellfish than others.
Do not eat Shark, Swordfish, King Mackerel, or Tilefish because they contain high levels of mercury. Eat up to 12 ounces (2 average meals) a week of a variety of fish and shellfish that are lower in mercury. Five commonly eaten fish that are low in mercury are shrimp, canned light tuna, salmon, pollock, and catfish. Albacore ( white ) tuna has more mercury than canned light tuna.. Check local advisories about the safety of fish caught by family and friends in your local lakes, rivers, and coastal areas.
Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes - ppt video online download

Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes - ppt video

Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes - ppt video online download

Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes - ppt video online download
Animals, Free Full-Text

Pisces: Definition, Classification and Characteristics

Fishes

Blank Page, Pollinator Habitat Conservation Along Roadways, Volume 4: Great Basin
Chapter 39 Fish With introduction to vertebrae classes - ppt video

Physiology and Pathophysiology of Itch

Computational modeling and analysis of the morphogenetic domain signaling networks regulating C. elegans embryogenesis - Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal

Tetrapod terrestrialisation: a weight-bearing potential already present in the humerus of the stem-tetrapod fish Eusthenopteron foordi

Spinosaurus is not an aquatic dinosaur

Ultrasonography and X-ray micro-computed tomography characterization of the effects caused by carrageenin in the muscle of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) - ScienceDirect
Hemichordate genomes and deuterostome origins